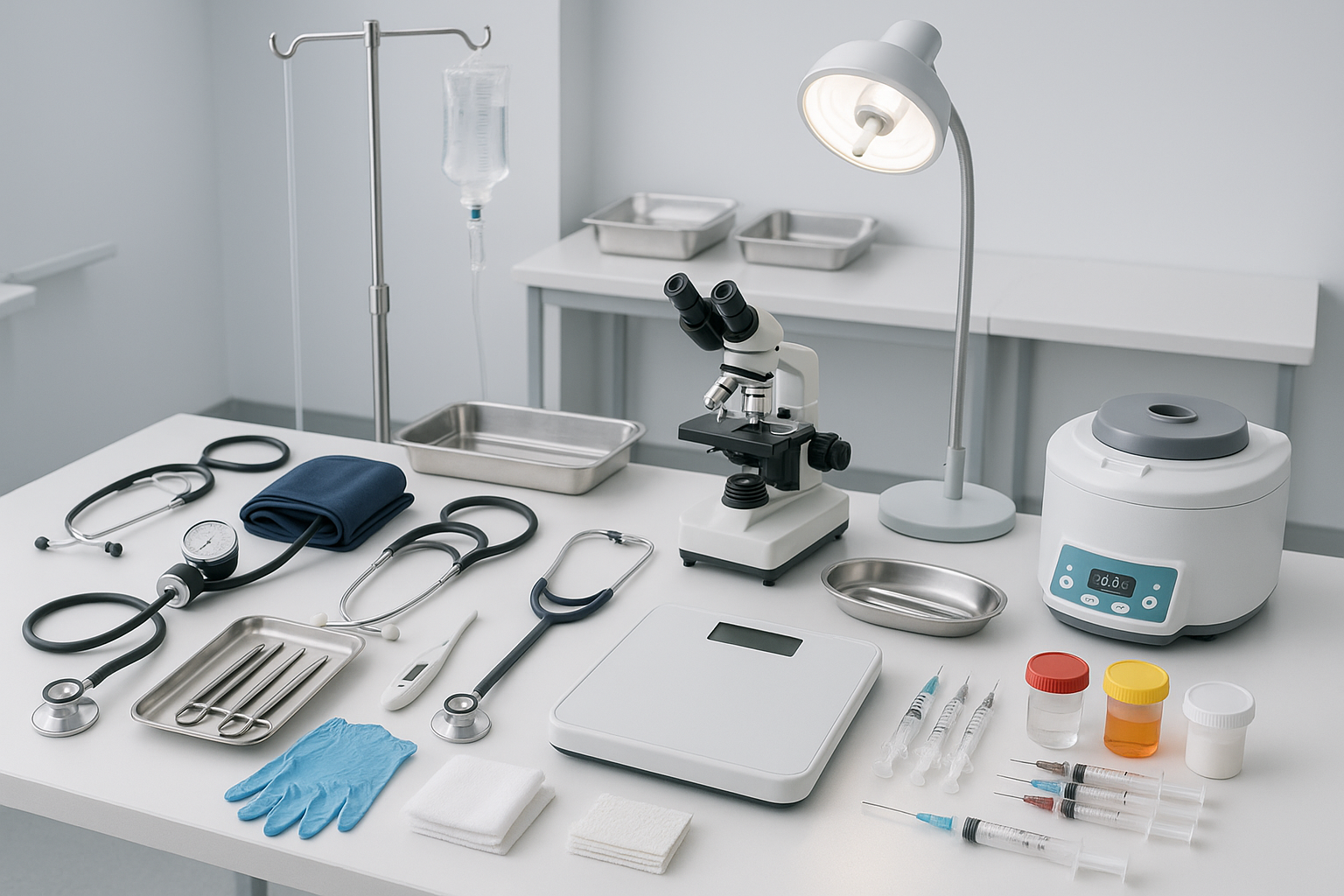
D Pharmacy Laboratory Equipment
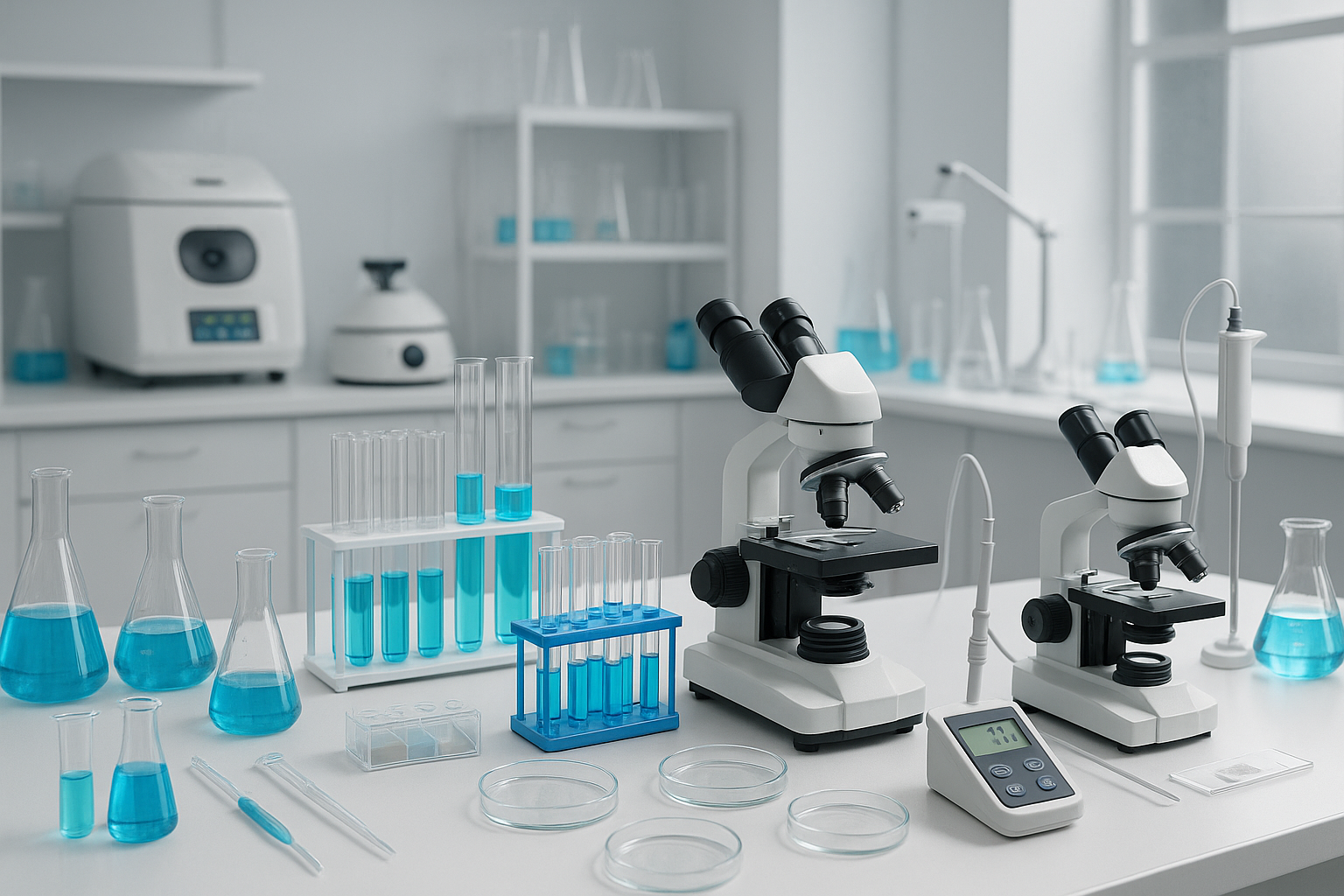
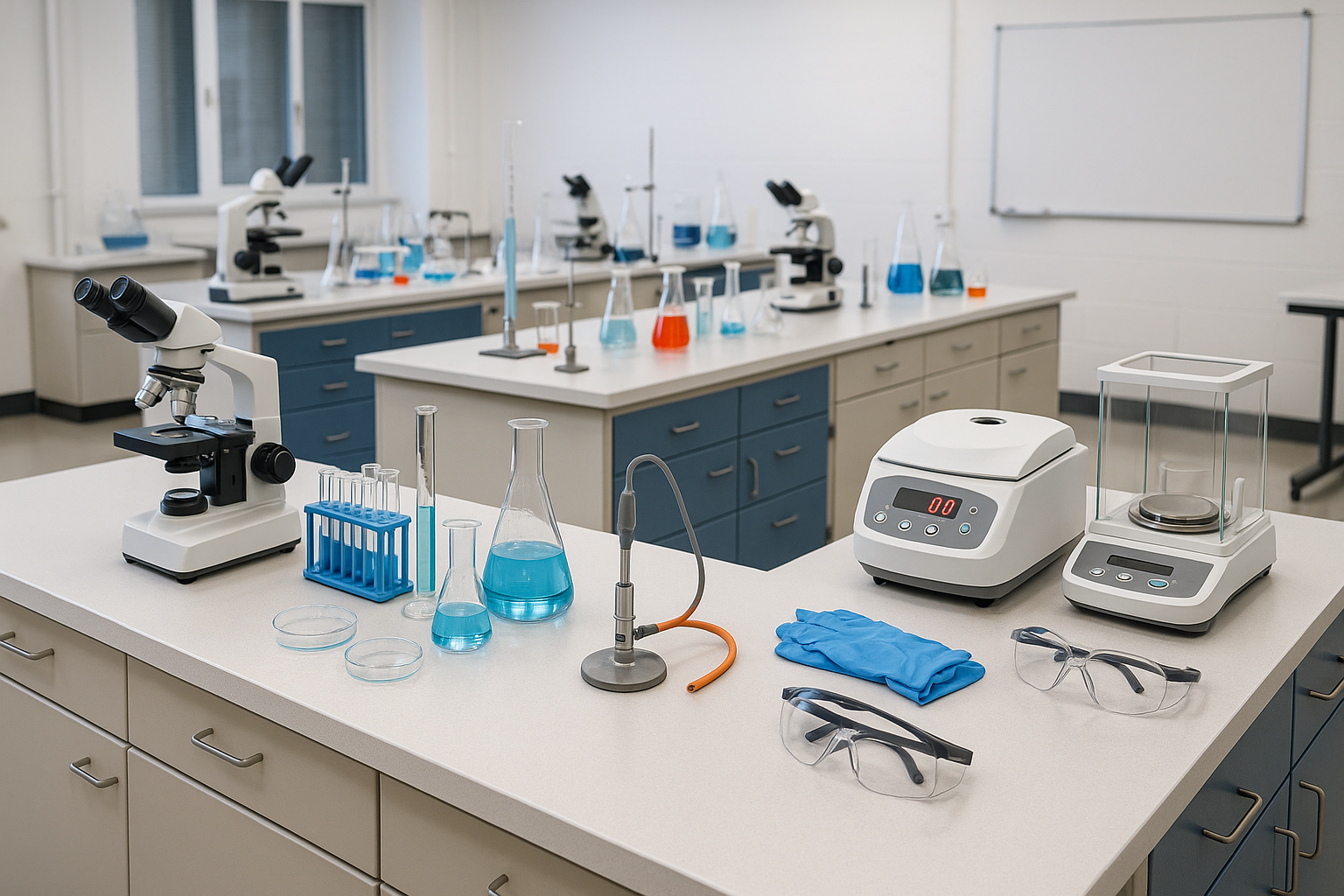
D Pharmacy laboratory equipment is crucial for students and professionals in the pharmacy field. This equipment includes a wide range of instruments and tools that facilitate the formulation, analysis, and testing of pharmaceutical products. In a D Pharmacy program, understanding and utilizing this equipment is essential for practical training and knowledge application.
-
Analytical balance: Used to measure the weight of chemicals and other substances.
-
Burette: Used to measure and dispense precise volumes of liquids.
-
Conical flask: Used for mixing, heating, and storing chemicals.
-
Pipettes: Used to dispense small amounts of liquid accurately.
-
Mortar and pestle: Used to grind and mix small amounts of chemicals.
-
Hot plate: Used for heating substances and solutions.
-
Beakers: Used for holding and measuring liquids.
-
Test tubes: Used for holding and mixing small amounts of liquids.
-
Funnel: Used for transferring liquids from one container to another.
-
Graduated cylinder: Used for measuring and dispensing precise volumes of liquids.
-
Thermometer: Used for measuring the temperature of substances.
-
Microscope: Used for examining small objects and organisms.
-
Separatory funnel: Used for separating two immiscible liquids.
-
Chromatography paper: Used for separating and identifying different components of a mixture.
-
Refractometer: Used for measuring the refractive index of a substance.
-
Spectrophotometer: Used for measuring the absorbance or transmittance of a substance.
-
pH meter: Used for measuring the acidity or basicity of a solution.
-
Ultrasonic cleaner: Used for cleaning lab equipment and tools.
-
Magnetic stirrer: Used for stirring solutions using a magnetic field.
-
Water bath: Used for heating samples and solutions indirectly in water.
The laboratory environment in a pharmacy school is designed to provide students with hands-on experience. Learning to work with D Pharmacy laboratory equipment enables students to grasp concepts such as drug formulation, quality control, and therapeutic applications. Essential equipment includes analytical balances, microscopes, centrifuges, and a variety of glassware.
Analytical balances are indispensable in any pharmacy laboratory. They are used to measure precise quantities of substances for compounding medications. The accuracy of an analytical balance affects the quality of the pharmaceutical products prepared. Each balance must be routinely calibrated to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Microscopes are another important piece of D Pharmacy laboratory equipment. They allow for the examination of samples at a microscopic level, which is crucial for quality control and research purposes. Students learn to use both light and electron microscopes, gaining insight into the physical characteristics of compounds.
Centrifuges play a vital role in the separation of substances based on density. In pharmacy labs, they are commonly used for separating plasma from blood or purifying compounds. Understanding how to operate centrifuges is a key skill for students in D Pharmacy programs.
Glassware, including beakers, flasks, and pipettes, is fundamental in any laboratory setting. Students need to become familiar with various types of glassware, as each serves a specific purpose in experiments and formulations. Proper usage and care of glassware is taught, emphasizing safety and accuracy in measurements.
In addition to these tools, D Pharmacy laboratory equipment includes safety equipment. This includes personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. A strong emphasis is placed on safety protocols to ensure that students understand the importance of maintaining a safe working environment.
Proper training in the use of D Pharmacy laboratory equipment prepares students for real-world pharmacy settings. Many laboratories and pharmacies rely on the skills acquired during D Pharmacy courses to ensure compliance with industry standards. Furthermore, experience with this equipment enhances employment prospects in the pharmaceutical industry.
Students also learn about the proper maintenance and calibration of D Pharmacy laboratory equipment. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure longevity and accuracy. Understanding how to troubleshoot common issues with lab equipment is also a crucial aspect of the curriculum.
Beyond the technical skills, students develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities through hands-on experience with laboratory equipment. This is vital in a field that demands precision and reliability. The ability to analyze data collected from experiments using D Pharmacy laboratory equipment is an invaluable skill for future pharmacists.
The integration of technology in pharmacy laboratories is also growing. Advanced instruments, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) systems, are becoming commonplace. Understanding and operating these advanced systems requires additional training and practice, but they are essential for modern pharmaceutical research.
As students progress in their D Pharmacy education, they may have opportunities to engage in research projects, which would require the use of all the laboratory equipment learned. This experience not only solidifies their understanding but also contributes to the field of pharmacy through innovative research.
In conclusion, D Pharmacy laboratory equipment forms the backbone of practical pharmacy education. Mastery of this equipment is crucial for anyone aspiring to be a pharmacist or work in the pharmaceutical industry. Through effective training and hands-on practice, students gain the skills needed to excel in their careers.