Categories
- 10 Best Bod Incubator in 2023
- 10 Best compound microscopes in 2023
- 10 Best Lab chemicals in 2023
- 10 Best Lab equipment suppliers in 2023
- 10 Best lab microscopes in 2023
- 10 Best Microbiology Lab Equipment in 2023
- 10 Best student microscopes In 2023 Lowest Price
- 10 Best vertical autoclaves in 2023
- Accessories
- Aerospace Engineering lab Equipment
- Agriculture College Lab Equipment Suppliers
- agriculture Lab Equipment
- Agronomy Lab Equipment
- analytical lab Equipment
- Anatomy lab equipment
- Animal House lab Equipment
- AUTOMOBILE LAB
- ayurvedic drug testing laboratory
- ayurvedic pharmacy instruments
- B pharmacy Equipments suppliers
- B. D. Instrumentation (India)
- Binocular Microscope
- Biochemistry lab equipment
- Biological Lab Equipment
- Biological Sciences lab Equipment
- Biomedical Engineering Lab Equipment
- Biophysics lab equipment
- Biostatistics Lab Equipment
- Biotechnology
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Borolab Scientific Glass Pvt. Ltd.
- Botany Lab Product
- BOTANY PERMANENT MICRO-PREPARED SLIDES
- CAD LAB
- Cardiology Lab Equipment
- Central Drug House (P) Ltd - CDH
- CENTRAL WORKSHOP
- Centre for Community Medicine lab equipment
- Centrifuge machine
- centrifuge machine suppliers in india
- Chemical Engineering Equipment
- Chemistry equipment
- Chemistry Lab Apparatus
- Chromatography Apparatus
- Civil Engineering
- Clean Air Equipment
- College of Nursing Lab Equipment
- D Pharmacy equipment
- Dairy lab instrument
- dental autoclave price
- Dental Equipment
- Department Of Anatomy Lab Equipment
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Equipment
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICS Equipment
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSY Equipment
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY Equipment
- Diffusion Cell Apparatus
- Digital Centrifuge Machine
- Distillation apparatus
- Do meter
- DYNAMICS OF MACHINES LAB
- EDM LAB equipment
- Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Lab Equipment
- Engineering Institute laboratory Equipment
- Engineering Laboratory Equipment
- ENT AND OPHTHALMIC
- Entomology Lab equipment
- equipment for laboratory
- Flash Point Apparatus
- FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY FLUID LAB
- FMS LAB
- Gastroenterology and Human Nutrition
- General Laboratory Equipment
- General Laboratory Equipment
- Genetics and Plant Breeding lab Equipment
- Genetics and Plant Breeding lab Equipment
- Haematology Lab Equipment
- Handi Centrifuge Machine
- Heart Models
- HEAT & MASS TRANSFER LAB
- Heating & Cooling Products
- herbal testing laboratory
- Hospital equipment
- Hospital equipment supplier near me
- Human Body Part Models
- Human Skeleton Model White PVC Plastic
- I.C. ENGINE LAB
- Industrial & Soil Equipment
- Kashmir Surgical Works
- Knee Joint Model
- Lab Chemical
- lab equipment
- Lab Fabric items
- lab plasticware
- lab water bath
- Laboratory Centrifuge
- Laboratory Consumables
- Laboratory equipment
- laboratory equipment
- Laboratory equipment manufacturers and suppliers
- Laboratory equipment suppliers in ambala cantt
- Laboratory equipment suppliers in Delhi
- Laboratory equipment suppliers in India
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers in Jaipur
- Laboratory glassware & Chemical Items
- laboratory instruments manufacturers in ambala cantt
- Labpro banner
- Labpro Banner 60%
- Labpro international
- Live Stock & Production Management lab Equipment
- Livestock & Production Management
- MATERIAL SCIENCE LAB
- MEASUREMENT & METROLOGY LAB
- measuring tools
- Mechanical Engineering
- Medical laboratory equipment suppliers
- medical mannequin
- medical products
- Mega Offers
- Melting Point Apparatus
- Metrological Lab Equipment
- Microbiological Diagnostic Equipment
- Microbiology & Pharmacology Laboratory Equipment
- Microbiology laboratory equipment
- Microcentrifuge
- Micrometer
- Micropipettes
- microscopes
- Milk Testing Equipment
- mushroom lab Equipment
- Nephrology lab equipment
- Nursing College Lab Equipment
- Nursing Department lab equipment
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology lab equipment
- Offer Zone
- Orthopaedics lab equipment
- OSAW INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS PVT LTD
- Otorhinolaryngology lab equipment
- Paediatrics lab equipment
- Pathology lab equipment
- Pediatric lab equipment
- PERMANENT SLIDES
- Pharma Analysis Laboratory Equipment
- Pharma Biology Laboratory Equipment
- PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY EQUIPMENT
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lab Equipment
- Pharmaceutical lab equipment & Research Lab Equipment
- Pharmaceutics Laboratory Equipment
- Pharmacognosy Laboratory Equipment
- Pharmacology lab equipment
- Pharmacy college lab equipment suppliers
- Pharmacy laboratories equipment
- Physical Pharmacy Lab equipment
- physics 60% Discount
- physics lab
- Physiology lab equipment
- Plant Pathology & Microbiology Lab
- product Offers 2023
- Profile Projectors
- Pusher Centrifuge
- RADICAL SCIENTIFIC EQUIPMENTS PVT LTD
- REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING LAB
- Reproductive Biology lab equipment
- Research Section lab equipment
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- School And College University equipment
- School And College University Products
- school lab equipment manufacturers in india
- Science Laboratory Equipment
- Scifa Laboratory equipment lnc
- SCITECH SCIENTIFICS
- Seed Technology
- Seed Technology Lab Equipment
- Silica Gel
- Skull Models
- soil testing instruments
- soil testing lab equipment list
- Soxhlet Extraction Apparatus
- SPAN AUTOMATION
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS LAB
- Table Top Centrifuge
- Testing Equipment
- Tiles Ceramic Laboratory Equipment
- Top manufacturers Laboratory fume hood in india
- types of mask
- Types of Microscopes
- Urology lab equipment
- Veterinary Sciences Lab Product
- Zoology Lab Equipment
Recent Articles
-
physics lab equipment 2024 February 04, 2024
-
How to use a Micropipette November 26, 2023
-
10 Top Uses for Water Baths August 24, 2023
Tag Cloud
Top Sellers
How to use a Micropipette
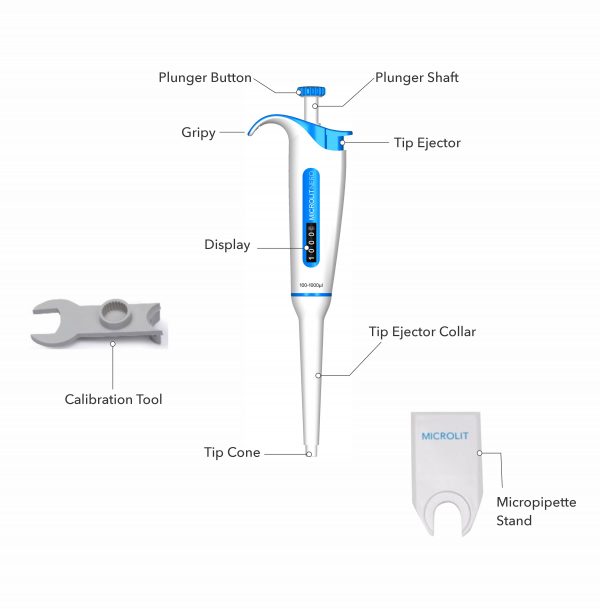
Single Channel Variable Volume Micropipette is a High Precision Micropipette that is designed with ergonomics in mind. It facilitates remarkable user experience and impeccable accuracy in practical laboratory environments. The product is highly recommended for Molecular biology, Microbiology, Immunology, cell culture, Analytical Chemistry, Biochemistry, Genetics etc. 1ml pipette is our most popular micropipette model followed by the 200ul pipette.
What’s in the box?
- Micropipette
- 3-4 compatible tips
- Pipette Calibration Tool
- Micropipette holder
- Pipette Calibration Certificate
- User guide
| Model No. | Description | Vol. Range(uL) | Increment(uL) | Accuaracy | CV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +% | +uL | +% | +uL | ||||
| BO-2 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 0.2-2µL | 0.2-2.0ul | 0.01 | 2 | 0.04 | 1.2 | 0.024 |
| BO-10 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 0.5-10µL | 0.5-10ul | 0.02 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.05 |
| BO-20 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 2-20µL | 2-20ul | 0.02 | 0.8 | 0.16 | 0.4 | 0.08 |
| BO-50 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 5-50µL | 5-50ul | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| BO-100 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 10-100µL | 10-100ul | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| BO-200 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 20-200µL | 20-200ul | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| BO-1000 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 100-1000µL | 100-1000ul | 1.0 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.2 | 2 |
| BO-5000 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 500-5000µL | 0.5-5ml | 10.0 | 0.6 | 30 | 0.2 | 10 |
| BO-10000 | Micropipette RBO Series Vol. Range 1-10ml | 1-10ml | 20.0 | 0.6 | 60 | 0.2 | 20 |
The error limits (Accuracy and Coefficient of Variation) mentioned above are in accordance with the nominal capacity (or maximum volume) indicated on the instrument. These are obtained by using the instrument with distilled water at equilibrium, the ambient temperature of 20 °C while operating it smoothly and steadily. The error limits are in accordance with DIN EN ISO 8655-2.
FAQs
To use the micropipette properly, there are a few steps that need to be followed:
- Set the desired volume of the micropipette.
- To aspirate, Press and hold the plunger at the first stop.
-
Place the tip in the liquid vertically.
Note: The angle should not exceed 20 degrees. With changing angle, the hydrostatic pressure inside the pipette tip varies. As a result, the aspirated volume will be inconsistent. It is best to immerse the pipette tips just below the surface (2-3 mm) of the liquid to allow the desired volume to be aspirated. Immersing the pipette tip too deeply increases the risk of liquid droplets sticking to the outside of the pipette tip.
- Release the plunger slowly to draw up the liquid into the tip.
- Pause, and then move the tip out from the liquid container carefully.
- Insert the tip into the delivery vessel.
- Make sure that the tip touches the inner wall of the vessel (it is recommended to tilt the tips at 45 degree for proper liquid release) and then press the plunger to the second stop.
- Pause, and then take the tip out from the vessel.
- Remove the tip with the help of the tip ejector when done with the experiment. For high precision, remember to change the tip frequently by ejecting into a waste container.
- Pharmaceuticals: It assists in various pharmaceutical experiments ranging from sampling and analysis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), impurities, excipients and pharmaceutical solutions to pharmaceutical starting materials, including finished pharmaceutical products (FPP).
- Health Care: It is essential in healthcare divisions such as blood banks and pathology labs to prepare blood and plasma samples to initiate any kind of testing.
- Food & Beverage: It requires in Research, Production and Analysis & Quality Control of food and its related products – especially Beverages & Drinking Water, Milk & Dairy Products and Edible Fats & Oils.
- Environmental Monitoring: Helps in different kind of testing related to soil, water and pollution control.
- Academic & Research Institutes: Gives the easy lab access to students and reasearchers in various life sciences applications including Cell and Tissue Culture, Microbiology, Biochemistry, Biology, Chemistry and Stem Cell Research.
- Diagnostic Kits: Micropipettes empower your Diagnostic Kits by offering a sophisticated blend of mobility and accuracy in pathogen detection, veterinary testing, meat speciation, fish speciation, GMO detection, allergen testing, etc.
- Life Sciences: Molecular biology research and related experiments like DNA RNA Purification, PCR, RT PCR, Primers & Probes, Cloning, Proteomics and Drug Discovery.
There are mainly two techniques of pipetting:
-
Forward pipetting technique: Forward pipetting is a technique for dispensing a precise amount of liquid by means of an air displacement pipette. The technique is primarily recommended for aqueous solutions, such as buffers, or dilute acids or alkalis.

- Reverse pipetting technique: Reverse pipetting is a technique for dispensing a precise amount of liquid by means of an air displacement pipette. This technique is mainly used for solutions with high viscosity or a tendency to foam as it minimizes the risk of splashing, foam, or bubble formation. Reverse piping is more accurate in dispensing small amounts of liquids containing proteins and biological solutions.
Micropipettes are accessible in numerous designs and sizes. In any case, there are certain components that are basic and common to all the micropipettes. These are:
- Plunger: It is mainly used to perform the two functions: Volume adjustment and Liquid aspiration/ dispensing
- Tip Ejector: In order to allow the safe, effortless, and quick ejection of tips, micropipettes are provided with a tip ejector.
- Volume Display: This shows the volume of the liquid to be aspirated or dispensed.
- Tipcone: The tipcone provides fitment to the tips. A micropipette with a universal tipcone is recommended because it increases the instrument’s compatibility with most of the standard tips.
- Gripy: It helps to support and hold the micropipette comfortably.
Micropipettes can be classified depending upon:
- As per Working Principle
- Air Displacement Micropipette: In an air displacement pipette, a small air cushion exists between the piston and the liquid solution during the process. These kinds of pipettes are extremely precise for a wide range of piping applications.
- Positive Displace Micropipette: With a positive displacement pipette, a piston replaces the air cushion and glides along the inner edges of the capillary for easy pipetting of viscous, dense and surfactant liquids.
- As per Operation Mechanism
- Mechanical Micropipette: These micropipettes are manually operated based on a piston-shaft spring mechanism.
- Electronic Micropipette: Electronic pipettes are more accurate than pipetting manually and mostly automated. Electronic pipettes remove the hand control one has over the pipette. The volume is set electronically, and with the push of a button, the plunger moves up and down electronically, leaving no room for human error.
- As per number of Channels
- Single Channel Micropipette: A single channel micropipette is one that has a single channel to aspirate or dispense the liquid.
- Multi Channel Micropipette: A multi-channel micropipette has multiple channels to aspirate or dispense the liquid. It is commonly available in 8 channel, 12 channel and 16 channel variants.
- As per Volume or Capacity
- Fixed Volume Micropipette: In a fixed volume micropipette, the volume of the liquid to be aspirated or dispensed remains constant. These micropipettes are used when the same amount of liquid has to be dispensed multiple times.
- Variable Volume Micropipette: This micropipette comes with a specific minimum and maximum volume range. The amount of liquid to be aspirated or dispensed can be adjusted (within the volume limit of the micropipette) based on the user’s requirement.
A micropipette is a common laboratory instrument used to measure small amounts of liquids with a volume range between 1 and 1000µl. A micropipette is also used to transfer a precise amount of fluid from one container to another.
Micropipettes are generally used in microbiology, chemistry, medical and soil testing laboratories for the precise transfer of different liquid samples. While the single channel micropipettes are used in labs that perform research related to molecular biology, microbiology, immunology, cell culture, analytical chemistry, biochemistry and genetics, the multichannel micropipettes are recommended for ELISA (diagnostic test), molecular screening, kinetic studies and DNA amplification.
Top Suppliers
Collections
- Dairy products
- Milk Testing Equipment
- physics lab
- Laboratory And Scientific Equi...
- microscopes
- ENT AND OPHTHALMIC
- measuring tools
- Centrifuge machine
- Micrometer
- Micropipette
- Silica Gel
- BOTANY PERMANENT MICRO-PREPARE...
- PERMANENT SLIDES
- centrifuge machine
- mask - type of mask
- medical products
- bod incubator
- Lab Chemical
- Do meter
- Lab Fabric items
- dental Autoclave
- medical mannequin
- White PVC Plastic Human Skelet...
- Human Body Part Models
- Heart Models
- Knee Joint Model
- Skull Models
- Laboratory Centrifuge
- Handi Centrifuges
- Microcentrifuge
- Table Top Centrifuge
- Digital Centrifuge Machine
- Pusher Centrifuge
- Laboratory Consumables
- Melting Point Apparatus
- Soxhlet Extraction Apparatus
- Distilling Apparatus
- Chemistry Lab Apparatus
- Chromatography Apparatus
- Diffusion Cell Apparatus
- Flash Point Apparatus
- Science Laboratory Equipment
- Profile Projectors
- Engineering Laboratory Equipme...
- Types of Microscopes
- General Laboratory Equipment
- Heating & Cooling Products
- Hospital equipment
- Testing Equipment
- Clean Air Equipment
- Engineering & Institute labora...
- HEAT & MASS TRANSFER LAB
- REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONI...
- I.C. ENGINE LAB
- FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY ...
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS LAB
- EDM LAB equipment
- MATERIAL SCIENCE LAB
- FMS LAB
- CAD LAB
- AUTOMOBILE LAB
- MEASUREMENT & METROLOGY LAB
- DYNAMICS OF MACHINES LAB
- CENTRAL WORKSHOP
- Aerospace Engineering lab Equi...
- Biological Sciences lab Equipm...
- Chemical Engineering Equipment
- Civil Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- School And College University ...
- Lab Glassware & Chemical Items
- Zoology Lab Equipment
- Microbiology laboratory equipm...
- Chemistry Lab Products
- Botany Lab Product
- Biological Lab Equipment
- Department Of Anatomy Lab Equi...
- College of Nursing Lab Equipme...
- Endocrinology, Metabolism & Di...
- Haematology Lab Equipment
- Orthopaedics lab equipment
- Pediatric lab equipment
- Pathology lab equipment
- Physiology lab equipment
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- Urology lab equipment
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology lab...
- Otorhinolaryngology lab equipm...
- Pharmacology lab equipment
- Anatomy lab equipment
- Research Section lab equipment
- Pharmaceutical & Research Lab ...
- Physical Pharmacy Lab equipmen...
- Pharma Biology Laboratory Lab ...
- General Laboratory Equipment
- School And College University ...
- Medical College Lab equipment
- Biomedical Engineering Lab Equ...
- Biostatistics Lab Equipment
- Cardiology Lab Equipment
- College of Nursing Lab Equipme...
- Gastroenterology and Human Nut...
- Gastroenterology and Human Nut...
- Nursing Department lab equipme...
- Paediatrics lab equipment
- Reproductive Biology lab equip...
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- Biochemistry lab equipment
- Biophysics lab equipment
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Centre for Community Medicine ...
- Nephrology lab equipment
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lab E...
- Microbiology & Pharmacology La...
- D Pharmacy equipment
- B pharmacy Equipments
- Pharmaceutics Laboratory Equip...
- Pharma Analysis Laboratory Equ...
- Animal House lab Equipment
- Pharmacognosy Laboratory Equip...
- Pharmacy laboratories equipmen...
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY Equ...
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSY Eq...
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICAL CHEMI...
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICS Equipm...
- PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY E...
- Livestock & Production Managem...
- Veterinary Sciences Lab Produc...
- Live Stock & Production Manage...
- Genetics and Plant Breeding la...
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Seed Technology Lab Equipment
- Genetics and Plant Breeding la...
- Biotechnology
- Seed Technology
- Soil Science & Soil Water Cons...
- Entomology Lab equipment
- Agronomy Lab Equipment
- Metrological Lab Equipment
- Plant Pathology & Microbiology...
- Dental Equipment
- Microbiological Diagnostic Equ...
- Industrial & Soil Equipment
- Accessories
- Mega Offer
- Offer Zone
- Tiles Ceramic Laboratory Equip...
- analytical lab Equipment
- ayurvedic drug testing laborat...
- ayurvedic pharmacy instruments
- herbal testing laboratory
- mushroom lab Equipment
- lab plasticware
- agriculture Lab Equipment
- Agriculture College Lab Equipm...
- Labpro Banner 60%
- Labpro banner
- physics 60% Discount
- Hospital equipment supplier Ne...
Top Suppliers
Blog Posts
- green laser Light...
- Student Stereo Mi...
- Binocular Microsc...
- Laboratory Equipm...
- Prokaryos lab and...
- Pharmacy Lab
- Micro lab Laminar...
- MILK TESTING EQUI...
- Micrometer
- Centrifuge Machin...
- Chemistry Lab Equ...
- Agricultural coll...
- full body sanitiz...
- hydrometer for wi...
- Portable Bottle f...
- Egg Incubator
- Laboratorydeal of...
- A complete list o...
- different types o...
- Uses of Microscop...























