Categories
- 10 Best Bod Incubator 2025 at Lowest Price
- 10 Best Compound Microscopes 2025 at Lowest Prices
- 10 Best Lab Chemicals 2025 at Lowest Prices
- 10 Best Lab Equipment Suppliers 2025 - Lowest Prices Available
- 10 Best Lab Microscopes 2025
- 10 Best Microbiology Lab Equipment 2025 at Lowest Prices
- 10 Best Refrigerator Mortuary Freezer India
- 10 Best Student Microscopes 2025 at Lowest Prices
- 10 Best Vertical Autoclaves 2025 - Vertical Autoclaves Best Prices 2025
- Accessories Collection: Trendy and Essential Items
- Aerospace Engineering Equipment Collection for Optimal Research and Innovation
- Agriculture Lab Equipment for Precision Farming and Research
- Agriculture Lab Equipment Suppliers for Agriculture College Needs
- Agronomy Lab Equipment for Precise Agricultural Research
- analytical lab equipment for precision testing and research
- Anatomy Lab Equipment Collection for Education and Research
- Animal House Lab Equipment: Essential Tools for Research
- AUTOMOBILE LAB: Explore Innovations in Automotive Engineering
- ayurvedic drug testing laboratory for quality assurance and effectiveness
- Ayurvedic Lab Equipment Suppliers and Manufacturers for Colleges
- Ayurvedic Pharmacy Instruments: Essential Ayurvedic Pharmacy Tools
- B Pharmacy Equipment Suppliers: Quality Supplies for Your Pharmacy
- B. D. Instrumentation India: Leading Solutions in Instrumentation
- Best Microscope for Students in India: Top Picks for Students
- Binocular Microscope Collection
- Biochemistry lab equipment
- Biological Lab Equipment Collection
- Biological Lab Equipment for Research and Experimentation in Biological Sciences
- Biology Lab Equipment
- Biomedical Engineering Lab Equipment
- Biophysics Lab Equipment for Research and Experiments - Essential Tools for Biophysics Studies
- Biostatistics Lab Equipment
- Biotechnology Collection: Innovative Advances in Biotechnology
- Biotechnology Lab Tools and Equipment for Advanced Research
- Biotechnology Lab Tools for Efficient Research and Innovation
- Borolab Scientific Glass Pvt. Ltd.
- Botany Lab Supplies for All Your Plant Research Needs
- Botany Permanent Micro-Prepared Slides Collection - Botany Micro-Prepared Slides
- CAD Lab Collection - Innovative Designs and Solutions
- Cardiology Lab Equipment
- Central Drug House Collection - CDH
- CENTRAL WORKSHOP Collection: Premium Tools and Equipment for Every Project
- Centre for Community Medicine Lab Equipment Collection
- Centrifuge Machine Collection: Explore Top Models and Features
- Centrifuge Machine Suppliers India - Quality and Reliability at Its Best
- Chemical Engineering Equipment Collection
- Chemistry equipment
- Chemistry Lab Apparatus - Essential Chemistry Lab Equipment
- Chromatography Apparatus Collection for Efficient Separation Techniques
- Civil Engineering Collection: Essential Resources and Insights
- Clean Air Equipment
- College of Nursing Lab Equipment
- D Pharmacy equipment
- Dairy Analysis Instruments: Essential Tools in the Dairy Lab Collection
- Dental Autoclave Cost and Price Analysis Collection
- Dental Equipment Supply and Tools for Professionals
- Department of Anatomy Lab Equipment – Essential Anatomy Lab Equipment for Students and Professionals
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Equipment - Pharmaceutical Chemistry Equipment
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICS Equipment - Pharmaceutical Equipment Collection
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSY Equipment - Essential Tools for Research and Analysis
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY Equipment
- Diffusion Cell Apparatus: Understanding Its Applications and Benefits
- Digital Centrifuge Machine Collection
- Distillation Equipment: Essential Distillation Apparatus for Your Collection
- Do Meter Collection: Unique Designs and Innovative Styles
- DYNAMICS OF MACHINES LAB: Comprehensive Resources for Understanding Machine Dynamics
- EDM LAB Equipment Collection: Essential EDM LAB Equipment for Your Needs
- Endocrinology Lab Equipment for Metabolism & Diabetes Research
- Engineering Institute Laboratory Equipment Collection - Engineering Laboratory Equipment
- Engineering Laboratory Equipment Collection: Essential Instruments and Tools
- ENT and Ophthalmic Conditions Collection
- Entomology Lab Equipment Essentials
- Flash Point Apparatus Collection for Accurate Testing
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Collection: Machinery Fluid Lab Experiments
- FMS LAB Collection - Explore Unique Innovatives
- Gastroenterology and Human Nutrition
- General Laboratory Equipment Collection for Efficient Research
- General Laboratory Equipment for Accurate Experiments and Analysis
- Genetics and Plant Breeding Equipment for Your Lab Needs
- Genetics and Plant Breeding Equipment: Essential Lab Tools for Research
- Haematology Lab Equipment: Essential Haematology Lab Instruments
- Handi Centrifuge Machines Collection
- Heart Models Collection: Unique Designs and Inspirations
- HEAT & MASS TRANSFER LAB
- Heating and Cooling Solutions for Optimal Comfort with Laboratory Equipment
- Herbal Products Quality Analysis in Herbal Testing Laboratory
- High-Quality Laboratory Equipment by Glomax - Leading Laboratory Equipment Manufacturer
- Hospital Equipment for Healthcare Professionals Collection
- Hospital Equipment Supplier Near Me: Your Local Source for Quality Medical Supplies
- Human Body Part Models Collection
- Human Skeleton Model - White PVC Plastic Educational Tool
- I.C. Engine Technology: Comprehensive Insights and Experiments in Internal Combustion Engine Lab
- Industrial Soil Equipment Collection: Essential Tools for Soil Management
- Kashmir Surgical Works - Quality Kashmir Surgical Instruments
- Knee Joint Model Collection
- Lab Chemicals: Essential Lab Chemical Supplies for Your Experiments
- Lab Equipment Collection: Essential Tools for Every Laboratory
- Lab Fabric Items Collection: Unique and Versatile Designs
- Lab Plasticware Supplies Collection for Laboratory Equipment and Supplies
- Lab Water Bath Collection: Essential Equipment for Precision Heating
- Laboratory Centrifuge Collection: Explore Top Laboratory Centrifuge Solutions
- Laboratory Consumables and Essential Laboratory Supplies
- Laboratory Equipment Collection: Essential Tools for Science and Research
- Laboratory Equipment Collection: Essential Tools for Your Experiments
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers Ambala Cantt - Quality & Variety Available
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers and Manufacturers Collection
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers Delhi: Top Providers in the Capital
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers India: Your Trusted Source
- Laboratory Equipment Suppliers Jaipur: Top Providers in the City
- Laboratory Equipment: Essential Tools for Every Laboratory
- Laboratory Glassware and Chemicals for Your Collection
- Laboratory Instruments Manufacturers Ambala Cantt
- Labpro Banner 60% Collection
- Labpro Banner Collection - Elevate Your Space with Unique Designs
- Labpro international
- Live Stock Management Equipment for Production Management Lab
- Livestock Production Management: Strategies for Effective Livestock and Production Management
- MATERIAL SCIENCE LAB - Explore Innovations in Material Science Lab
- Measurement and Metrology Lab Collection
- Measuring Tools for Precision: Accurate Measurements and Precision
- Mechanical Engineering Techniques: A Comprehensive Collection
- Medical laboratory equipment suppliers
- Medical Mannequin Collection for Training and Education
- Medical Supplies and Products Collection
- Mega Offers Discounts: Unbeatable Deals and Discounts Collection
- Melting Point Apparatus Collection
- Metrological Lab Equipment for Accurate Measurements and Testing
- Microbiological Diagnostic Equipment for Accurate Testing
- Microbiology and Pharmacology Equipment Collection
- Microbiology Laboratory Equipment and Zoology Lab Equipment
- Microcentrifuge Collection: Essential Tools for Precision Lab Work
- Micrometer: Explore Our Unique Micrometers Collection
- Micropipettes for Lab Use Collection
- Microscopes for Tiny Details: Explore the World of Tiny Details
- Milk Testing Equipment Collection: High-Quality Solutions for Accurate Results
- Mushroom Lab Equipment for Cultivation and Research
- Nephrology Lab Equipment: Essential Tools for Renal Research
- Nursing Lab Equipment Collection for Nursing College
- Nursing Lab Equipment for Nursing Department Collection
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology Equipment for Enhanced Care in Lab Settings
- Offer Zone: Exclusive Deals and Discounts Collection
- Orthopaedics Lab Equipment Collection
- OSAW Industrial Products Pvt Ltd - Quality Industrial Solutions
- Otorhinolaryngology Lab Equipment Collection
- Paediatrics Lab Equipment for Accurate Diagnosis and Care
- Pathology Lab Equipment for Accurate Diagnostics
- Pediatric Lab Equipment: Essential Tools for Child Healthcare
- PERMANENT SLIDES Collection for Lasting Impact
- pH meters for research - Top-Rated pH Meters for Accurate Testing
- Pharma Analysis Equipment for Laboratory Use
- Pharma Lab Equipment Collection for Enhanced Research Productivity
- Pharmaceutical and Research Lab Equipment Collection
- PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY EQUIPMENT
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lab Equipment Collection
- Pharmaceutics Laboratory Equipment Collection
- Pharmacognosy Lab Equipment Collection
- Pharmacology Lab Equipment: Essential Pharmacology Lab Tools
- Pharmacy Lab Equipment Suppliers for Quality Pharmacy College Tools and Supplies
- Pharmacy Laboratory Equipment Collection
- Physical Pharmacy Physics Lab Equipment Collection
- Physics Discount Items - 60% Off Select Products
- Physics Lab: Engaging Physics Lab Experiments for All Levels
- Physiology Lab Equipment for Essential Experiments
- Plant Pathology Microbiology Lab Collection
- product Offers 2024
- Profile Projectors: Precision Measurement Tools for Accurate Profile Analysis
- Pusher Centrifuge Collection: Innovative Solutions for Efficient Separation
- RADICAL SCIENTIFIC EQUIPMENTS PVT LTD - Radical Scientific Equipment Collection
- Refrigerated Centrifuge Suppliers and Manufacturers Collection
- REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING LAB
- Reproductive Biology lab equipment
- Research Section Lab Equipment - Essential Research Lab Equipment for Your Needs
- Rheumatology Lab Equipment and Rheumatology Lab Supplies
- Rheumatology Lab Tools for Accurate Diagnosis and Efficient Testing
- School and College Equipment Collection
- School and College University Products Collection for All Your Needs
- school lab equipment manufacturers in india
- Science Laboratory Equipment Collection for All Your Needs
- Scifa Laboratory Equipment: Innovative Solutions for Your Lab Needs
- SCITECH SCIENTIFICS: Advancing Scitech Scientific Research
- Seed Technology Collection: Innovations in Seed Technology
- Seed Technology Lab Equipment for Advanced Seed Technology Equipment Solutions
- Silica Gel Collection: Unique and Versatile Silica Gel Products
- Skull Models Collection: Unique and Intricate Designs
- Soil Testing Instruments Collection
- soil testing lab equipment list
- Soxhlet Extraction Solutions for Efficient Solvent Extraction Apparatus
- Span Automation - Span Automation Solutions for Efficient Processes
- spectrophotometer
- Strength of Materials Lab: Unleashing Structural Integrity
- Table Top Centrifuge Collection: Premium Table Top Centrifuges for Precision Lab Use
- Testing Equipment Collection
- Tiles Ceramic Laboratory Equipment: Optimize Your Ceramic Laboratory Tiles Equipment for Effective Analysis
- Top Laboratory Fume Hood Manufacturers in India - Leading Laboratory Fume Hood Manufacturers India
- Types of Masks: Explore Various Types of Masks
- Types of Microscopes: A Comprehensive Guide to Different Microscope Types
- Urology lab equipment
- Veterinary Lab Products for Optimal Veterinary Sciences Lab Solutions
- Zoology Lab Equipment: Essential Zoology Lab Instruments
Recent Articles
Tag Cloud
Top Sellers
Laboratory Equipment List: Essential Tools for Every Lab

Laboratory Equipment List: Essential Tools for Every Lab
The Laboratory Equipment List is crucial for anyone setting up or maintaining a laboratory. A well-curated laboratory equipment list ensures that researchers and technicians have the necessary tools to conduct experiments, perform analyses, and maintain laboratory safety standards. Different laboratories may require varied equipment depending on their specific functions, be it for chemical, biological, or physical experiments.
A laboratory equipment list is a comprehensive inventory of all the tools, instruments, apparatus, and devices used in a laboratory setting to conduct experiments, research, and various scientific activities. It serves as a crucial resource for lab managers, researchers, and technicians to ensure that they have all the necessary equipment to carry out their work efficiently and safely. Below is a description of some common categories of laboratory equipment:
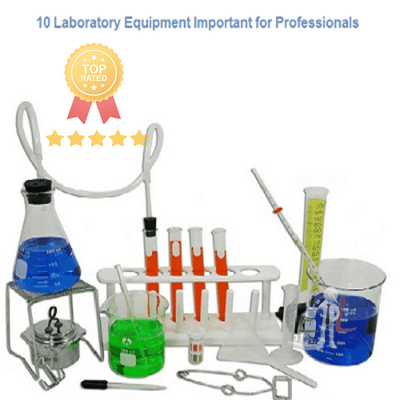 1. Glassware:
1. Glassware:-
-
- Beakers: Cylindrical containers with flat bottoms used for mixing, heating, and measuring liquids.
- Flasks: Vessels with a narrow neck and a flat or round bottom, used for holding and mixing liquids.
- Test tubes: Small cylindrical tubes used to hold and heat small quantities of liquids or for various tests.
- Graduated cylinders: Tall, narrow containers with calibrated markings used for precise volume measurements.
-
-
Instruments for Measurement:
- Thermometers: Devices to measure temperature accurately, crucial for experiments involving temperature-sensitive reactions.
- Balances: Precision instruments used to measure mass or weight of substances.
- pH meters: Tools to measure the acidity or alkalinity of solutions.
- Pipettes and burettes: Devices used to accurately measure and transfer specific volumes of liquids.
-
Heating and Cooling Equipment:
- Bunsen burners: Gas burners used for heating substances in the laboratory.
- Hot plates: Electrically heated plates used for controlled heating of liquids or solid samples.
- Incubators: Devices used to maintain a controlled environment for culturing cells or biological samples.
- Refrigerators and freezers: Used for storage of temperature-sensitive reagents and samples.

-
Safety Equipment:
- Safety goggles and lab coats: Protective gear to prevent contact with hazardous chemicals or substances.
- Fume hoods: Enclosed workspaces with exhaust systems to protect users from harmful fumes and vapors.
- Fire extinguishers: Used in case of accidental fires in the lab.
-
Microscopes and Imaging Equipment:
- Compound microscopes: Instruments used to magnify small objects, such as cells or microorganisms.
- Centrifuges: Machines that spin samples at high speeds to separate components based on density.
- Spectrophotometers: Devices used to measure the intensity of light transmitted or absorbed by a sample.

-
Miscellaneous Equipment:
- Stirrers and magnetic stir bars: Used for stirring solutions without introducing contamination.
- Water baths: Containers filled with water, used to maintain a stable temperature for samples.
- Autoclaves: Machines that use high-pressure steam to sterilize equipment and media.
The specific equipment found in a laboratory will vary based on the nature of the research or experiments conducted there. A well-maintained and up-to-date equipment list ensures the lab operates efficiently, avoids downtime, and meets safety standards.
Basic laboratory equipment includes glassware like beakers, flasks, and test tubes, which are foundational for any lab experiment. Beakers are typically used for mixing, stirring, and heating substances. Flasks, on the other hand, come in different shapes and sizes, such as Erlenmeyer flasks, which assist in minimizing evaporation during reactions. Test tubes are essential for conducting smaller-scale experiments and are widely used in educational settings as well.
In addition to glassware, a laboratory equipment list must include measuring instruments like balances and pipettes. Analytical balances provide precision for weighing samples, which is vital for accurate results in quantitative experiments. Pipettes are indispensable for transferring liquids in specific volumes, enabling researchers to conduct precise measurements essential for experimental reproducibility.
Besides measuring tools, safety equipment is paramount in a laboratory environment. Safety goggles, gloves, and lab coats protect personnel from hazardous materials and accidents. It's essential to emphasize safety and ensure that all lab personnel wear the appropriate protective gear while handling chemicals or biological agents. Safety showers and eyewash stations should also be part of the laboratory equipment list, as they provide immediate assistance in case of spills or splashes.
Moreover, fume hoods play a significant role in ventilation, allowing toxic fumes to be safely vented away from the workspace, thus ensuring a safer environment for researchers. Incorporating a fume hood in the laboratory design is a critical aspect of any laboratory equipment list related to chemical handling.
For biological laboratories, incubators and refrigerators are essential. Incubators provide a controlled environment for growing cultures and cells, maintaining specific temperatures and CO2 levels. Refrigerators keep sensitive biological samples and reagents at optimal temperatures, preventing degradation and ensuring reliability during experiments.
In addition to these, centrifuges are remarkable pieces of equipment used to separate substances of different densities by spinning them at high speeds. They can be found in most biological and chemical labs, essential for processes such as DNA extraction and cell separation.
Furthermore, analytical equipment such as spectrophotometers and chromatographs are valuable tools for laboratory analysis. Spectrophotometers allow the quantification of substances by measuring light absorbance, which is important in many biochemical assays. Chromatographs, used for separating mixtures, play a pivotal role in chemical analysis, providing insights into the composition of substances.
Finally, every laboratory should maintain an inventory management system for its equipment, ensuring that all tools are accounted for, maintained, and replaced as needed. This also aids in facilitating efficient workflow and resource management within the lab environment.
In summary, a comprehensive Laboratory Equipment List encompasses glassware, measuring instruments, safety gear, ventilation systems, incubators, centrifuges, and analytical devices. Each aspect of this list is interlinked, contributing to a functional and safe laboratory space conducive to high-quality research and experimentation.
Top Suppliers
Collections
- Dairy products
- Milk Testing Equipment
- physics lab
- Laboratory And Scientific Equi...
- microscopes
- ENT AND OPHTHALMIC
- measuring tools
- Centrifuge machine
- Micrometer
- Micropipette
- Silica Gel
- BOTANY PERMANENT MICRO-PREPARE...
- PERMANENT SLIDES
- centrifuge machine
- mask - type of mask
- medical products
- bod incubator
- Lab Chemical
- Do meter
- Lab Fabric items
- dental Autoclave
- medical mannequin
- White PVC Plastic Human Skelet...
- Human Body Part Models
- Heart Models
- Knee Joint Model
- Skull Models
- Laboratory Centrifuge
- Handi Centrifuges
- Microcentrifuge
- Table Top Centrifuge
- Digital Centrifuge Machine
- Pusher Centrifuge
- Laboratory Consumables
- Melting Point Apparatus
- Soxhlet Extraction Apparatus
- Distilling Apparatus
- Chemistry Lab Apparatus
- Chromatography Apparatus
- Diffusion Cell Apparatus
- Flash Point Apparatus
- Science Laboratory Equipment
- Profile Projectors
- Engineering Laboratory Equipme...
- Types of Microscopes
- General Laboratory Equipment
- Heating & Cooling Products
- Hospital equipment
- Testing Equipment
- Clean Air Equipment
- Engineering & Institute labora...
- HEAT & MASS TRANSFER LAB
- REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONI...
- I.C. ENGINE LAB
- FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY ...
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS LAB
- EDM LAB equipment
- MATERIAL SCIENCE LAB
- FMS LAB
- CAD LAB
- AUTOMOBILE LAB
- MEASUREMENT & METROLOGY LAB
- DYNAMICS OF MACHINES LAB
- CENTRAL WORKSHOP
- Aerospace Engineering lab Equi...
- Biological Sciences lab Equipm...
- Chemical Engineering Equipment
- Civil Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- School And College University ...
- Lab Glassware & Chemical Items
- Zoology Lab Equipment
- Microbiology laboratory equipm...
- Chemistry Lab Products
- Botany Lab Product
- Biological Lab Equipment
- Department Of Anatomy Lab Equi...
- College of Nursing Lab Equipme...
- Endocrinology, Metabolism & Di...
- Haematology Lab Equipment
- Orthopaedics lab equipment
- Pediatric lab equipment
- Pathology lab equipment
- Physiology lab equipment
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- Urology lab equipment
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology lab...
- Otorhinolaryngology lab equipm...
- Pharmacology lab equipment
- Anatomy lab equipment
- Research Section lab equipment
- Pharmaceutical & Research Lab ...
- Physical Pharmacy Lab equipmen...
- Pharma Biology Laboratory Lab ...
- General Laboratory Equipment
- School And College University ...
- Medical College Lab equipment
- Biomedical Engineering Lab Equ...
- Biostatistics Lab Equipment
- Cardiology Lab Equipment
- College of Nursing Lab Equipme...
- Gastroenterology and Human Nut...
- Gastroenterology and Human Nut...
- Nursing Department lab equipme...
- Paediatrics lab equipment
- Reproductive Biology lab equip...
- Rheumatology lab equipment
- Biochemistry lab equipment
- Biophysics lab equipment
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Centre for Community Medicine ...
- Nephrology lab equipment
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lab E...
- Microbiology & Pharmacology La...
- D Pharmacy equipment
- B pharmacy Equipments
- Pharmaceutics Laboratory Equip...
- Pharma Analysis Laboratory Equ...
- Animal House lab Equipment
- Pharmacognosy Laboratory Equip...
- Pharmacy laboratories equipmen...
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY Equ...
- DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSY Eq...
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICAL CHEMI...
- DEPARTMENT OF P'CEUTICS Equipm...
- PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY E...
- Livestock & Production Managem...
- Veterinary Sciences Lab Produc...
- Live Stock & Production Manage...
- Genetics and Plant Breeding la...
- Biotechnology lab equipment
- Seed Technology Lab Equipment
- Genetics and Plant Breeding la...
- Biotechnology
- Seed Technology
- Soil Science & Soil Water Cons...
- Entomology Lab equipment
- Agronomy Lab Equipment
- Metrological Lab Equipment
- Plant Pathology & Microbiology...
- Dental Equipment
- Microbiological Diagnostic Equ...
- Industrial & Soil Equipment
- Accessories
- Mega Offer
- Offer Zone
- Tiles Ceramic Laboratory Equip...
- analytical lab Equipment
- ayurvedic drug testing laborat...
- ayurvedic pharmacy instruments
- herbal testing laboratory
- mushroom lab Equipment
- lab plasticware
- agriculture Lab Equipment
- Agriculture College Lab Equipm...
- Labpro Banner 60%
- Labpro banner
- physics 60% Discount
- Hospital equipment supplier Ne...
Top Suppliers
Blog Posts
- green laser Light...
- Student Stereo Mi...
- Binocular Microsc...
- Laboratory Equipm...
- Prokaryos lab and...
- Pharmacy Lab
- Micro lab Laminar...
- MILK TESTING EQUI...
- Micrometer
- Centrifuge Machin...
- Chemistry Lab Equ...
- Agricultural coll...
- full body sanitiz...
- hydrometer for wi...
- Portable Bottle f...
- Egg Incubator
- Laboratorydeal of...
- A complete list o...
- different types o...
- Uses of Microscop...
- Tags: 10 laboratory apparatus 10 laboratory apparatus and their uses 10 laboratory equipment 20 laboratory apparatus and their uses 2nd hand lab equipment agriculture lab equipment list all chemistry lab equipment names and pictures all lab equipment all lab equipment names and pictures all lab instruments all laboratory apparatus all laboratory equipment apparatus used in chemistry lab apparatus used in chemistry laboratory apparatus used in laboratory basic chemistry lab equipment basic lab equipment basic laboratory apparatus Beakers best laboratory equipment companies best place to sell used lab equipment bio lab equipment biological equipment biological instruments biological laboratory equipment biology lab equipment biology lab equipment list biology lab equipment list pdf biology lab equipment names biology lab equipment price list biology lab materials biotech lab equipment blood test equipment list blood test equipment price blood test lab equipment blood test machine price Bunsen burners buy lab equipment buy lab glassware buy laboratory equipment online buy used lab equipment Centrifuges cheap chemistry glassware cheap lab equipment cheap lab glassware chem lab equipment chem lab equipment names chem lab suppliers chemical apparatus and their uses chemical equipment list chemical lab equipment chemical lab equipment names chemical laboratory apparatus chemical laboratory equipment chemical laboratory instruments chemistry apparatus chemistry apparatus and their uses chemistry devices chemistry equipment chemistry equipment list chemistry equipment shop near me chemistry experiment equipment chemistry gear chemistry instruments chemistry instruments names chemistry items chemistry lab accessories chemistry lab apparatus chemistry lab apparatus and their uses chemistry lab equipment chemistry lab equipment buy online chemistry lab equipment for sale chemistry lab equipment glassware chemistry lab equipment list chemistry lab equipment list pdf chemistry lab equipment list with pictures chemistry lab equipment names chemistry lab equipment names and pictures chemistry lab equipment near me chemistry lab equipment price list chemistry lab equipment shop chemistry lab equipment shop near me chemistry lab equipment with pictures chemistry lab glass equipment chemistry lab instrument name chemistry lab instruments chemistry lab materials chemistry lab supplies chemistry lab supply store near me chemistry lab tools chemistry laboratory chemistry laboratory apparatus chemistry laboratory apparatus and their uses chemistry laboratory apparatus and their uses with pictures pdf chemistry laboratory equipment chemistry laboratory equipment list chemistry laboratory equipment list pdf chemistry laboratory instruments chemistry supplies chemistry supplies near me chemistry supply store chemistry supply store near me chemistry tools chemistry tools and equipment chemistry tools in lab chemistry tools list clinical lab equipment list consumable lab supplies different laboratory apparatus equipment for laboratory equipment used in chemistry lab experiment equipment fisher lab supplies fisher scientific lab supplies food lab equipment Fume hoods general lab equipment general lab supply general laboratory equipment glass lab equipment glass lab equipment names glass laboratory equipment Glassware Graduated cylinders hospital lab equipment list Hot plates instrument in laboratory instrument lab instruments laboratory instruments used in chemistry lab instruments used in laboratory lab accessories Lab apparatus lab apparatus and their uses lab apparatus list lab chemical suppliers lab chemical suppliers near me Lab coats lab consumables lab consumables list lab consumables suppliers lab equipment lab equipment and their uses lab equipment and uses lab equipment co lab equipment companies lab equipment cost lab equipment distributor lab equipment distributors in usa lab equipment for sale lab equipment glassware lab equipment list lab equipment manufacturers lab equipment manufacturers in india lab equipment names lab equipment names and pictures lab equipment names and pictures and uses lab equipment names and uses lab equipment near me lab equipment near me. laboratory equipment lab equipment parts lab equipment price list lab equipment service lab equipment shop near me lab equipment store lab equipment store near me lab equipment suppliers lab equipment suppliers in india lab equipment suppliers near me lab equipment website Lab gear lab glassware near me lab glassware shop near me lab glassware suppliers lab instruments Lab instruments checklist lab instruments list lab instruments name lab instruments name list lab instruments shop near me Lab inventory lab items lab machine price lab machinery lab maintenance lab material list lab material name lab material shop near me lab materials lab measuring equipment lab objects lab product lab safety equipment lab safety supply lab stuff Lab supplies lab supplies near me lab supplies online lab supplies scientific lab supply company lab supply distributors lab supply shop lab supply store lab supply store near me lab testing equipment lab testing equipment list lab testing equipment suppliers Lab tools lab tools and equipment lab usa lab utensils laboratory accessories laboratory apparatus laboratory apparatus and equipment laboratory apparatus and their uses laboratory apparatus and their uses with pictures laboratory appliances laboratory chemical suppliers laboratory consumables laboratory consumables and chemical supplies laboratory device Laboratory equipment laboratory equipment and instruments laboratory equipment company laboratory equipment for sale laboratory equipment glassware laboratory equipment list laboratory equipment list and their uses laboratory equipment list pdf laboratory equipment list with pictures laboratory equipment manufacturer laboratory equipment near me laboratory equipment price laboratory equipment services laboratory equipment shop near me laboratory equipment st laboratory equipment stores near me laboratory equipment suppliers laboratory equipment suppliers near me laboratory equipments and their uses laboratory glassware and equipment laboratory glassware suppliers laboratory glassware suppliers near me laboratory instruments laboratory instruments list laboratory instruments name laboratory items laboratory lab laboratory machine laboratory machine price in india laboratory machines laboratory maintenance laboratory materials laboratory materials and equipment laboratory parts laboratory product laboratory products list laboratory products online laboratory props laboratory shop near me laboratory stuff laboratory supplies laboratory supplies and equipment laboratory supplies near me laboratory supply store laboratory supply store near me laboratory testing equipment laboratory things laboratory tools laboratory tools and equipment list of laboratory apparatus machines used in chemistry lab Measurement devices mechanical lab equipment medical and lab supplies medical and laboratory equipment medical lab equipment medical lab equipment list medical lab equipment suppliers medical lab instruments medical lab supplies medical laboratory apparatus medical laboratory consumables medical laboratory equipment medical laboratory equipment list medical laboratory equipment list and their uses medical laboratory equipment price list medical laboratory instruments medical laboratory machines medical laboratory supplies Microscopes mini laboratory equipment name of laboratory equipment new lab equipment old lab equipment old lab equipment for sale pathology equipment pathology equipment price pathology lab equipment pathology lab equipment list pathology lab equipment list with price pathology lab equipment price list pathology lab instruments pathology lab machine price pathology laboratory equipment pathology machine pathology machine price pathology products physics lab equipment physics lab equipment for schools physics lab equipment price list physics lab equipment shop near me physics lab equipment suppliers Pipettes plastic lab equipment Refrigerators and freezers refurbished lab equipment Safety equipment Safety goggles science apparatus science chemistry lab equipment science equipment store near me science equipment suppliers science lab accessories science lab apparatus science lab equipment science lab equipment for schools science lab equipment list science lab equipment names science lab equipment names and pictures science lab equipment price list science lab equipment shop near me science lab instruments science lab materials science lab supplies science lab supplies near me science lab things science lab tools science laboratory apparatus science laboratory equipment science laboratory equipment list science laboratory tools science materials list science shop near me science supplies science supplies near me science supplies store science supply store near me science tools and equipment scientific apparatus scientific equipment scientific equipment shop near me scientific equipment supplier scientific equipment suppliers Scientific instruments scientific lab equipment scientific lab equipment manufacturer scientific lab supplies scientific laboratories supplies scientific laboratory equipment scientific store near me scientific supplies scientific supplies near me scientific supply store scientific supply store near me scientific tools list second hand lab equipment second hand lab equipment for sale sell lab equipment sell used lab equipment suppliers of lab equipment surplus lab equipment testing equipment list thermo fisher equipment thermo fisher lab equipment Thermometers things in a lab tools used in laboratory usa lab usa lab equipment used lab used lab equipment used lab equipment for sale used laboratory equipment used laboratory equipment for sale used scientific equipment we buy used lab equipment wholesale lab equipment
