Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus Uses and Their Applications
Chemistry laboratory apparatus uses are essential for conducting experiments and research in the field of chemistry. Understanding the various equipment and their specific functions can greatly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of experiments. This blog post will delve into the diverse chemistry laboratory apparatus uses and explain their applications, providing a comprehensive overview that caters to both students and professionals in the field. From basic tools to advanced instruments, each piece of equipment serves a unique purpose that is critical to successful experimentation.
Chemistry laboratory apparatus refers to the various tools and equipment used in a chemistry laboratory to carry out experiments, measure quantities, and perform chemical reactions. These apparatus are designed to facilitate the handling, manipulation, and analysis of chemicals and substances in a controlled and safe manner.
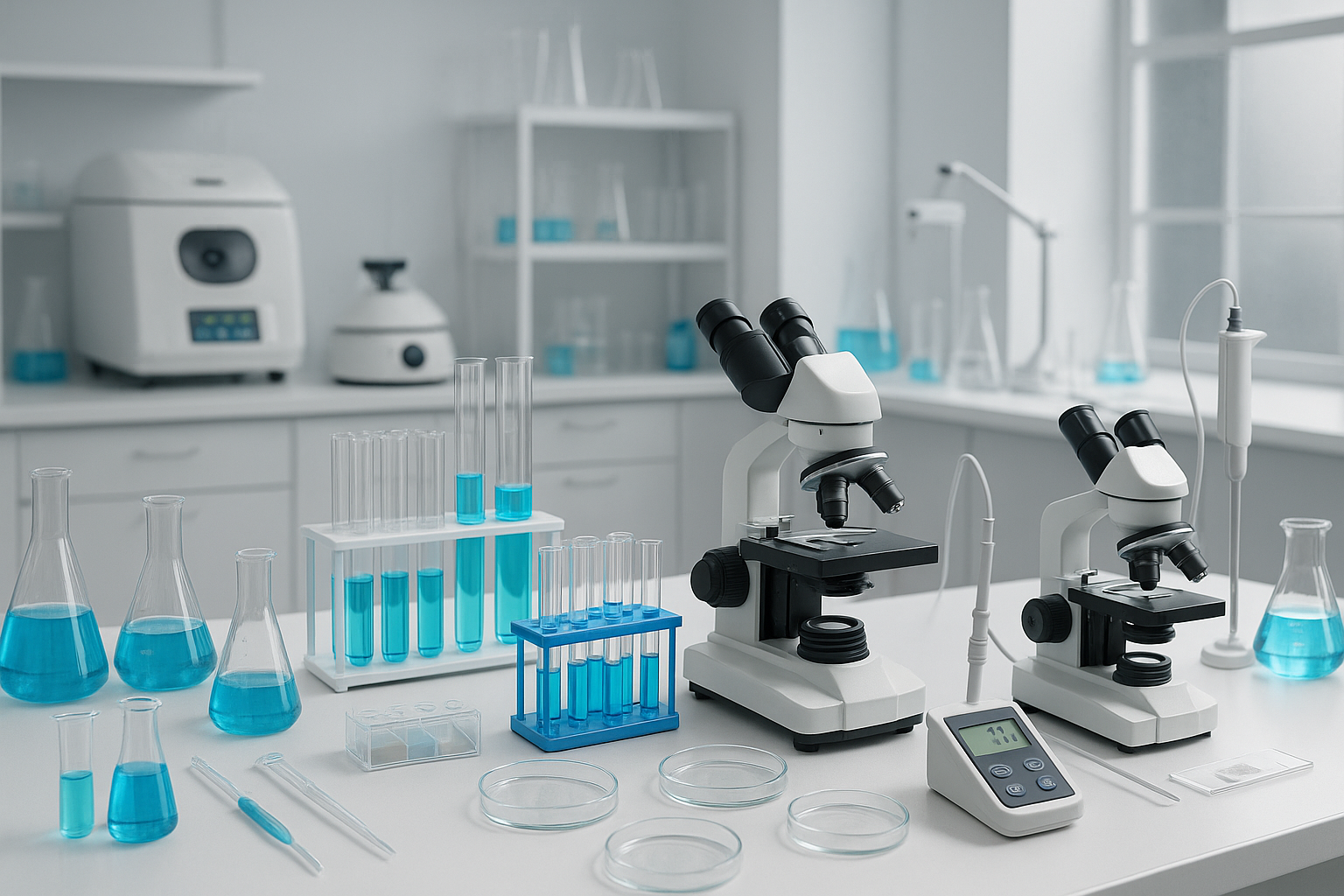
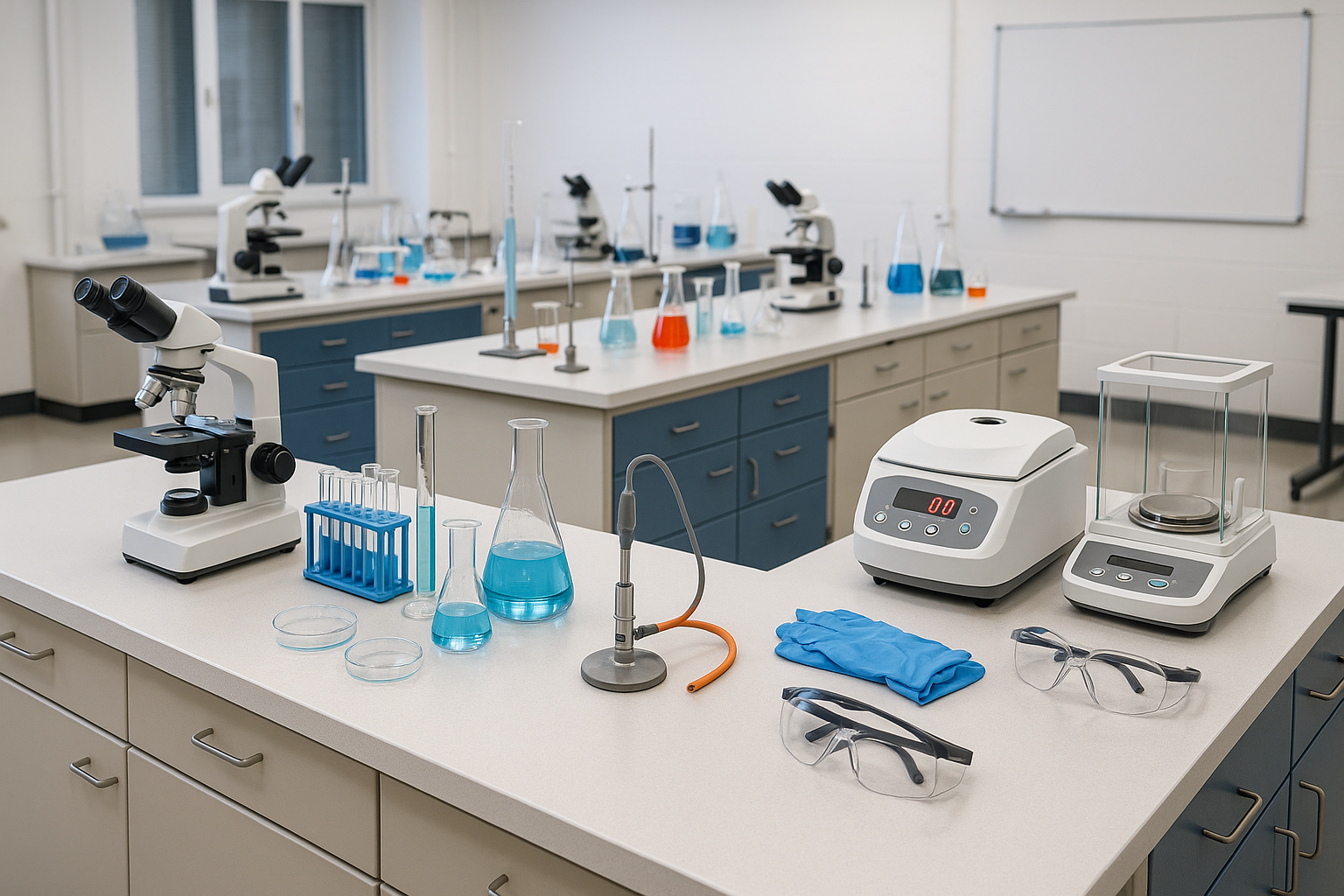
One of the most common pieces of apparatus found in a chemistry lab is the beaker. Beakers are cylindrical containers with a flat bottom and a spout for pouring. They are used for mixing, heating, and holding liquids during experiments. Graduated cylinders are similar in shape to beakers but have more precise volume measurements, making them ideal for accurate volume measurements.
Test tubes are another essential apparatus in a chemistry lab. They are small, cylindrical glass tubes with open tops. Test tubes are commonly used for heating small amounts of substances, conducting chemical reactions, and observing color changes or precipitate formations.
Pipettes are used for precise measurement and transfer of liquids. They come in various forms, such as graduated pipettes and micropipettes, and are essential for accurate dispensing of liquids in small volumes.
Bunsen burners are gas burners used for heating purposes. They provide a controlled flame for tasks like heating solutions, sterilizing equipment, or performing flame tests. Bunsen burners are often connected to gas supplies and can be adjusted to produce different flame types.
Other common chemistry apparatus include flasks (such as Erlenmeyer flasks and Florence flasks) for holding and mixing larger volumes of liquids, crucibles for high-temperature reactions, funnels for filtration and transferring liquids, and various types of glassware like watch glasses, petri dishes, and evaporating dishes.
In addition to glassware, chemistry laboratories also utilize a range of instruments for measuring and analyzing substances. These may include balances for precise weighing, pH meters for measuring acidity or alkalinity, spectrophotometers for analyzing the absorption or emission of light, and various types of chromatography equipment for separating and analyzing mixtures.
It is crucial to note that the selection and use of laboratory apparatus depend on the specific experiment or analysis being performed. Safety precautions, such as the use of protective gear, proper handling of chemicals, and adherence to standard operating procedures, are essential when working with laboratory apparatus to ensure the well-being of researchers and accurate results.
uses
- Beaker: Used for holding, mixing, and heating liquids during experiments.
- Test tube: Used for conducting chemical reactions, observing color changes, and heating small amounts of substances.
- Pipette: Used for precise measurement and transfer of liquids.
- Bunsen burner: Used for heating purposes, such as heating solutions, sterilizing equipment, or performing flame tests.
- Flask (e.g., Erlenmeyer flask, Florence flask): Used for holding and mixing larger volumes of liquids.
- Graduated cylinder: Used for accurate volume measurements of liquids.
- Crucible: Used for high-temperature reactions, such as heating substances to extremely high temperatures or melting metals.
- Funnel: Used for filtration and transferring liquids from one container to another.
- Watch glass: Used as a cover for evaporating dishes or for holding small amounts of substances.
- Petri dish: Used for culturing and observing microorganisms or for small-scale reactions.
- Evaporating dish: Used for evaporating solvents to concentrate substances or to create solid residues.
- Balance: Used for precise weighing of substances.
- pH meter: Used for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
- Spectrophotometer: Used for analyzing the absorption or emission of light by a substance.
- Chromatography equipment: Used for separating and analyzing mixtures based on their components' differential migration.
- Safety precautions: Refers to measures taken to ensure the safety of researchers and minimize risks in the laboratory.
- Standard operating procedures: Guidelines and protocols that dictate proper handling, usage, and maintenance of laboratory apparatus and ensure consistent and safe practices.
1. Beakers: Beakers are versatile glass containers used to hold, mix, and heat liquids. They come in various sizes and are marked with graduation lines to measure volumes accurately. Their designs facilitate easy pouring and mixing of chemicals.
2. Flasks: There are several types of flasks, including Erlenmeyer flasks and volumetric flasks. Erlenmeyer flasks have a narrow neck, which minimizes evaporation and allows for easy stirring. Volumetric flasks are used to prepare solutions with precise volumes.
3. Pipettes: Pipettes are used to transport a measured volume of liquid. They come in various forms, including graduated pipettes and volumetric pipettes, enabling precise measurement for experiments.
4. Burettes: Burettes are used in titration experiments, allowing for the precise dispensing of liquid reagents. They are crucial for calculating concentrations and determining how much reactant is needed to complete a reaction.
5. Test Tubes: Test tubes are used for mixing, heating, or holding small amounts of substances. They are essential for conducting small-scale experiments and observing reactions.
6. Spatulas: Spatulas are used to transfer solid chemicals from one container to another. Their flat design allows for easy scooping and scraping of materials.
7. Thermometers: Thermometers measure the temperature of substances, which is a crucial aspect of many chemical reactions. Different types, such as digital or glass thermometers, are used depending on the required precision.
8. Hot Plates: Hot plates are heating devices that provide a consistent heat source for experiments. They are safer and more convenient than open flames.
9. Centrifuges: Centrifuges separate substances of different densities by spinning them at high speeds. This process is used in various applications, including purifying samples and separating blood components.
10. Balances: Balances are essential for accurately measuring the mass of substances. Electronic balances provide precise measurements and are commonly used in laboratory settings.
11. Fume Hoods: Fume hoods are ventilation systems designed to protect laboratory personnel from inhaling hazardous fumes. They are crucial when working with volatile chemicals.
12. Safety Equipment: Personal protective equipment, such as lab coats, goggles, and gloves, ensures safety while handling chemicals. Awareness of safety procedures is vital to prevent accidents.
13. Refrigerators and Freezers: Chemists use refrigerators and freezers to store chemicals and samples at controlled temperatures, preserving their integrity for future experiments.
14. Stirrers: Magnetic stirrers and mechanical stirrers mix solutions thoroughly. They provide a constant stirring action, ensuring homogeneity in mixtures.
15. Chromatography Equipment: Chromatography techniques are used for separating chemical mixtures. Equipment like columns and analyzers enhances the separation process in research and quality control.
16. pH Meters: pH meters measure the acidity or alkalinity of solutions. This measurement is critical in many chemical reactions and processes.
17. Glassware: Various types of glassware, such as petri dishes and watch glasses, are used throughout experiments. They provide a non-reactive surface for various reactions.
In conclusion, understanding chemistry laboratory apparatus uses is vital for conducting experiments effectively and safely. Each piece of equipment plays a significant role in the various applications within the field of chemistry, enabling researchers and students to explore, innovate, and discover. By familiarizing yourself with these tools and their functions, you can enhance your laboratory skills and contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge.