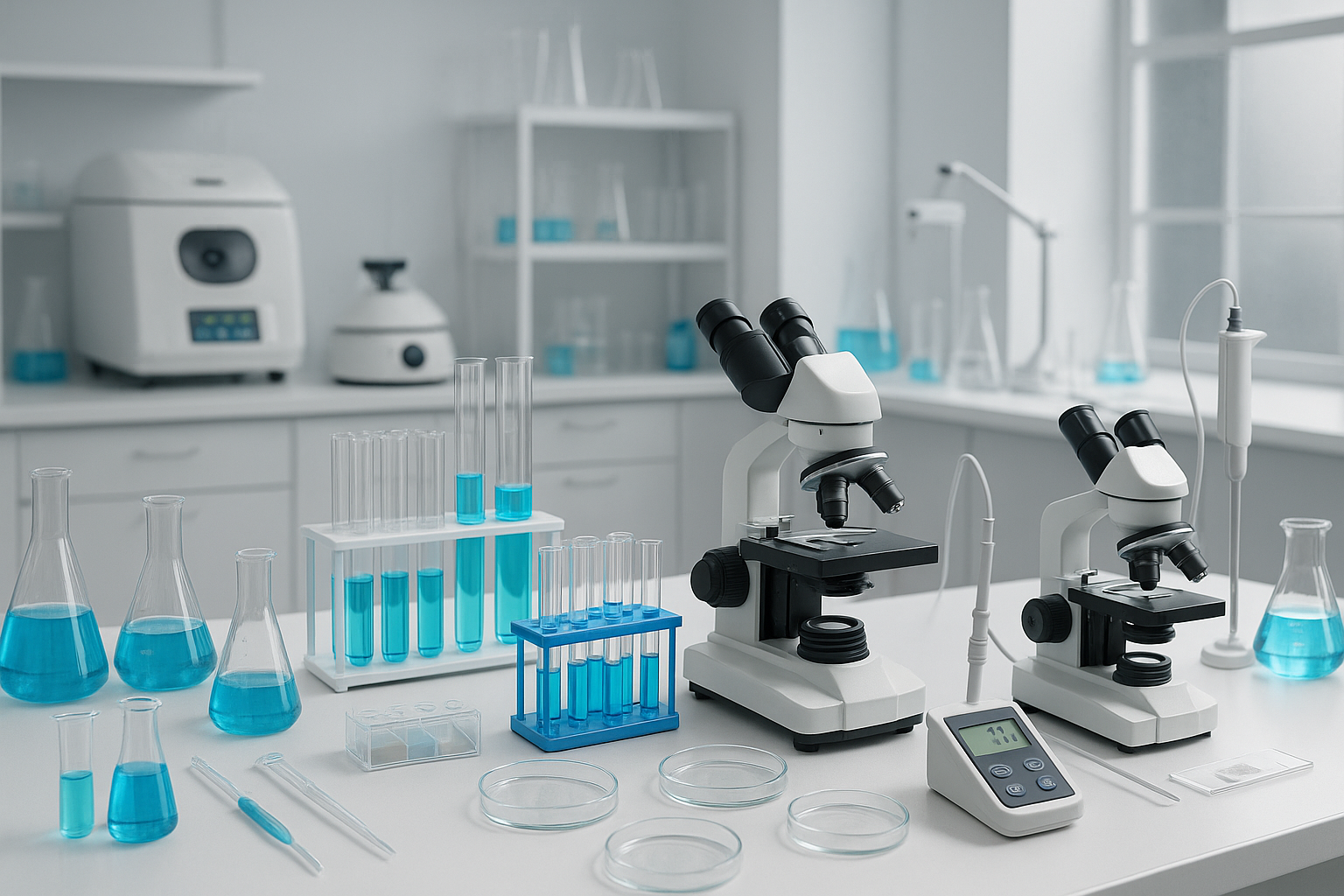
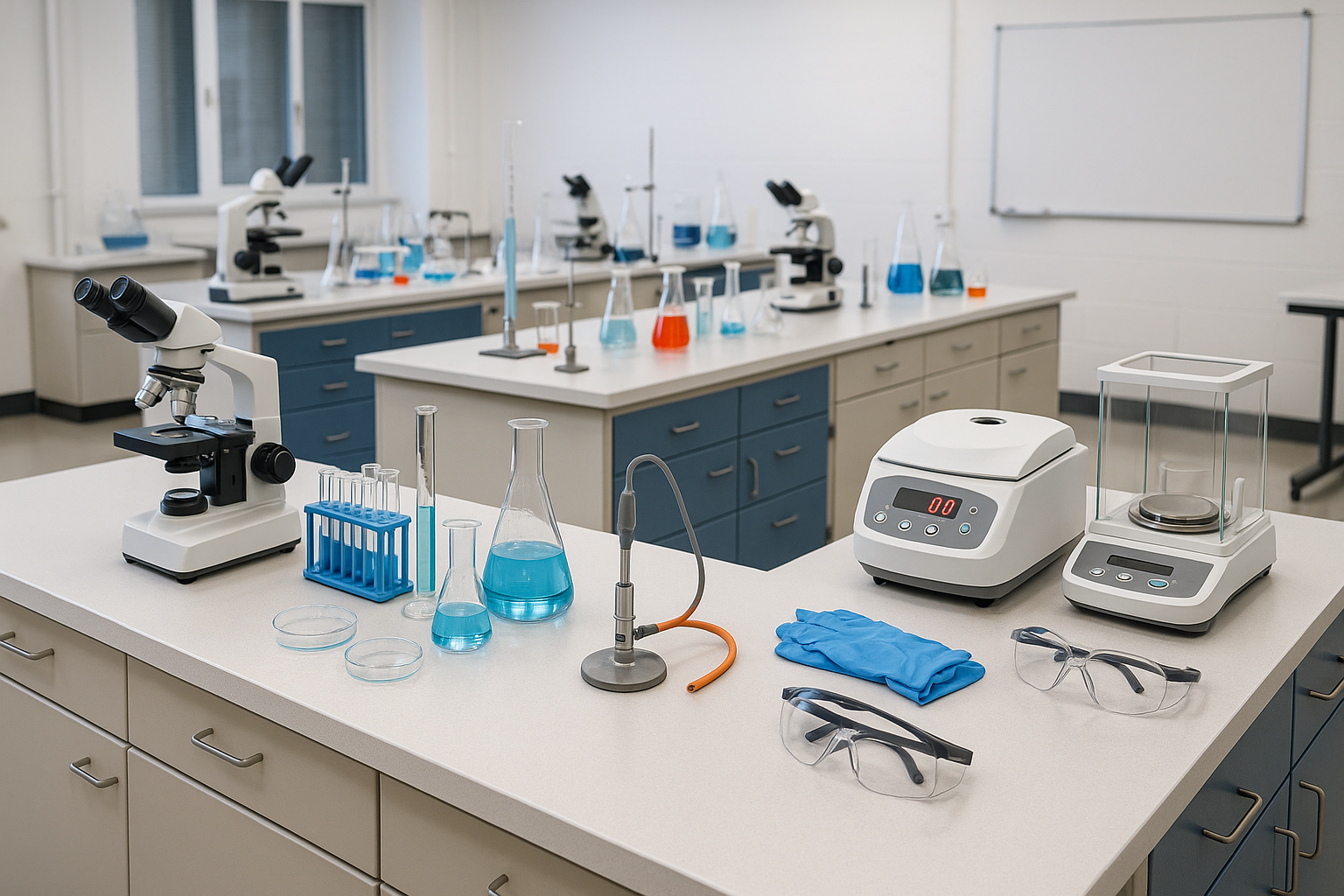
35 laboratory apparatus and their uses
-
Bunsen Burner:

A gas burner used for heating and sterilizing substances in the laboratory.
-
Beaker:

A cylindrical container with a flat bottom used for holding and measuring liquids.
-
Erlenmeyer Flask:

A conical-shaped flask used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids.
-
Test Tube:

A small cylindrical container used for holding small amounts of liquids or conducting small experiments.
-
Petri Dish:

A shallow, circular dish with a lid used for culturing microorganisms or small-scale experiments.
-
Pipette:
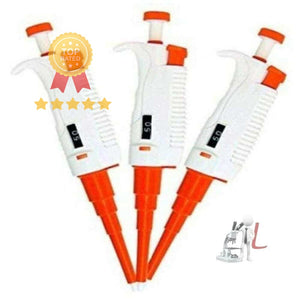
A slender tube used to transfer small quantities of liquids with precision.
-
Graduated Cylinder:

A tall, narrow container with calibrated markings used to measure the volume of liquids accurately.
-
Volumetric Flask:

A flask with a precise volume calibration, used to prepare accurate solutions.
-
Thermometer:

An instrument for measuring temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
-
pH Meter:

An electronic device used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
-
Funnel:

A conical-shaped tool used for pouring liquids into containers with small openings.
-
Mortar and Pestle:

Used for grinding and pulverizing solid substances into fine powders.
-
Microscope:

Used to view small objects or specimens at a high magnification.
-
Centrifuge:

A machine that spins samples at high speeds to separate components based on density.
-
Filter Paper:
A porous paper used to separate solids from liquids through filtration.
-
Water Bath:

A container filled with water used to maintain a constant temperature for samples.
-
Hot Plate:

A flat heating surface used to heat containers or substances.
-
Desiccator:

A sealed container with a drying agent used to keep substances dry.
-
Autoclave:

Used for sterilizing equipment and media by applying high-pressure steam.
-
Incubator:

Maintains a controlled environment for the growth and cultivation of microorganisms.
-
Spectrophotometer:

Measures the absorbance or transmittance of light by a sample, used for quantitative analysis.
-
Colorimeter:

Measures the intensity of a color and is used for colorimetric analysis.
-
Gas Chromatograph:

Analyzes and separates gases in a mixture for identification and quantification.
-
Liquid Chromatograph: Separates and analyzes liquid mixtures based on their components.
-

Measures the refractive index of a liquid, which helps identify substances.
-

Automates the process of titration for precise volumetric analysis.
-
Microplate Reader: Used to measure absorbance or fluorescence in microplates for high-throughput assays.
-

Creates a vacuum for various applications like filtration or drying.
-

Heats materials at high temperatures for sterilization or drying.
-

Uses a magnetic field to stir solutions without the need for a physical stirring rod.
- Melating point:

Determines the melting point of solid substances.

Separates components of a liquid mixture based on their boiling points.
33. Conductivity Meter:

Measures the electrical conductivity of a solution, indicating its ionic strength.
34. Gas Measuring Cylinder: Measures and dispenses precise volumes of gases.
35. Geiger-Muller Counter: Detects and measures radioactivity in samples.
These laboratory apparatus are essential for conducting various experiments, analyses, and research in different scientific fields.
LABPRO INTERNATIONAL Specializes in supplying a wide range of laboratory instruments, including physics lab equipment.
Offers both standard and customized products for educational institutions and research labs.
SCIFA LABORATORY EQUIPMENT INC. Offers various lab equipment, including items for physics labs like spectrometers, optical benches, and other measuring devices.
Provides good after-sales support and services for schools, colleges, and universities.
Laboratory Deal
1st Floor, A-Block, Flat No-105, Virani Lake Mist, Varthur
Road,
Whitefield, 5th Cross, Siddapura
Bengaluru Karnataka 560066
India
Mobile : 9034101997
well-known supplier of lab equipment across India, including Bengaluru.
Offers physics lab essentials like voltmeters, ammeters, galvanometers, and apparatus for experiments in mechanics, electricity, and optics.
Supplies a broad range of physics lab instruments such as pendulums, prisms, lenses, and force measurement devices.
Known for offering competitive prices and durable products.
School Kit physic, chemistry, biology, science, math : Ready to Packing
Ready To Dispatch Big Pracel : Bluedart, DHL, Fedax, Ecom, Delhvery, DTDC. Extra
Ready To Dispatch Small Pracel : Bluedart, DHL, Fedax, Ecom, Delhvery, DTDC. Extra
Lab setup And Installation : laboratorydeal








7 comments
Mallam J
You day ma
Wofai eteng inah
It really helped me thnks
Favor
Rogged
Otaba saviour
Nice explanation wow,wow,geogeous
Laura
Quite very good